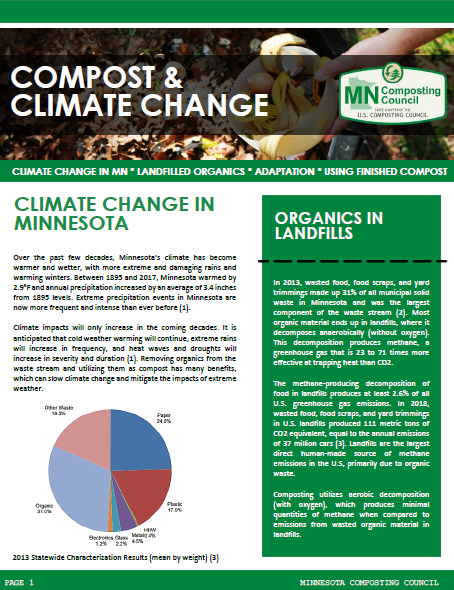
Resources for Compost Sites
Source-separated organics composting facilities in Minnesota
|
Drone footage of windrow turning at the SMSC facility 2020. (via Dustin Montey)
* indicates composter's products are tested and included in the USCC's STA program |
STA Certified Compost
Customers can buy compost with confidence through the US Composting Council Seal of Testing Assurance program. Composters participating in the Seal of Testing Assurance Certification program are required to meet strict standards at their facilities, ensuring only high-quality compost is being produced.
|
Source-separated organics composters who participate in the STA program are identified by an asterisks (*) above.
The following composters also participate in the USCC's STA program, but do not accept food scraps as feedstock:
The following composters also participate in the USCC's STA program, but do not accept food scraps as feedstock:
- OTI, Inc.: 2201 107th Ln. NE, Blaine, MN 55449
- Specialized Environmental Technologies (SET) - multiple yard waste facilities around the Twin Cities Metro
- Sustane Natural Fertilizer, Inc.: 310 Holiday Ave E, Cannon Falls, MN 55009
Certified Compost Operations Manager (CCOM)
Compost operators with one year of experience are eligible to participate in the USCC's Certified Compost Operations Manager program. Through this nationally recognized program, participants can expect to learn how to run a safe, effective compost site that utilizes current best management practices, all while gaining professional development experiences as compost site operators. For more information, visit the US Composting Council Certification Commission website. |
MNCC Compost Use Factsheets
MNDOA Noxious Weed Information listed by category
Compost Sampling Guidance Videos
The US CCREF in collaboration with many companies and individuals created two videos to serve as guides for employees responsible for collecting and sending compost samples to testing labs. Watch the videos below to learn how to properly sample compost with basic and advanced techniques, and how to troubleshoot compost quality issues due to operational procedures.
Compost Marketing Tools - Cornell Poster Web Page
These posters describe how compost can be used in different applications to improve the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of soils. There are multiple uses for compost including in agricultural production; on athletic fields; in gardening; for turf establishment and/or maintenance; in landscaping and tree planting; and in nurseries. Compost is a perfect medium for reclamation and remediation; for slope stabilization, erosion control and storm water management; and for roadsides, street trees and medians. Compost made in urban environments can and should be used locally to revitalize the urban environment.
Agricultural applications
Gardening-Vegetable applications
General Highway Uses
Reclamation Uses
Roadside Tree Planting
Slope Stabilization
Urban Environment Uses
Avian Flu Management
The MPCA solid waste and feedlot programs provided assistance and resources requested for the avian flu epidemic clean-up and disposal in Minnesota in 2015. The Minnesota Board of Animal Health (BAH) has the lead role in dealing with livestock emergency response cases and carcass disposal. In cases “where disposal may adversely affect ground or surface water, (the BAH) shall seek the input of PCA” (M.S. 35.815). The Minnesota Department of Agriculture was also extensively involved, and the Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service of the U.S. Department of Agriculture provided the federal response.
For more information on the Avian Flu epidemic in Minnesota, visit:
USDA
MPCA - Scroll to "Specialized Topics" Heading
Board of Animal Health
DNR
For more information on the Avian Flu epidemic in Minnesota, visit:
USDA
MPCA - Scroll to "Specialized Topics" Heading
Board of Animal Health
DNR
State Composting Rules

On November 18, 2014 The Minnesota Pollution Control Agency's Citizen Board unanimously recommended adoption of the proposed amendment to the States compost rule. Minnesota Rules and Regulations for compost facilities can be found through the MPCA.
The MN Composting Council continually provided comments to the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency throughout the Compost Rule revision process. Comments and letters from the MNCC and other Stakeholders can be found on our Advocacy webpage.
The State of Minnesota recognizes these four tiers of composting facilities:
1. Backyard Compost Site (no permit required)
2. Small Compost Site (no greater than 120 yards)
3. Yard Waste Composting Facilities (Permit By Rule)
4. Source-Separated Organic Material Composting Facilities (MPCA Permit Required)
The MNCC and the Association of Recycling Managers (ARM) created a Model Backyard and Small Composting Site Ordinance for municipalities to refer to when updating or creating ordinances for their community.
The MN Composting Council continually provided comments to the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency throughout the Compost Rule revision process. Comments and letters from the MNCC and other Stakeholders can be found on our Advocacy webpage.
The State of Minnesota recognizes these four tiers of composting facilities:
1. Backyard Compost Site (no permit required)
2. Small Compost Site (no greater than 120 yards)
3. Yard Waste Composting Facilities (Permit By Rule)
4. Source-Separated Organic Material Composting Facilities (MPCA Permit Required)
The MNCC and the Association of Recycling Managers (ARM) created a Model Backyard and Small Composting Site Ordinance for municipalities to refer to when updating or creating ordinances for their community.